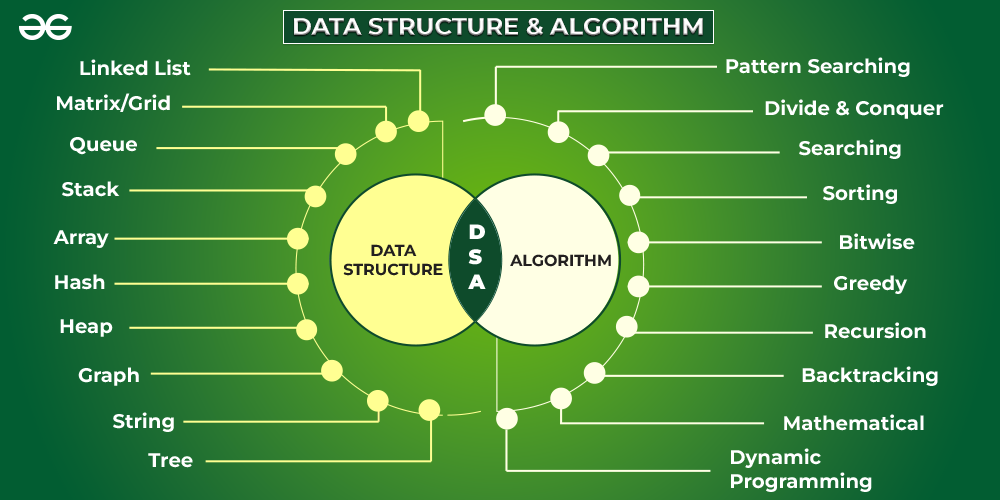
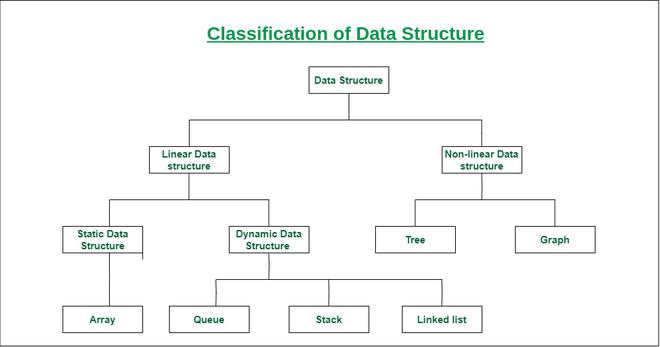
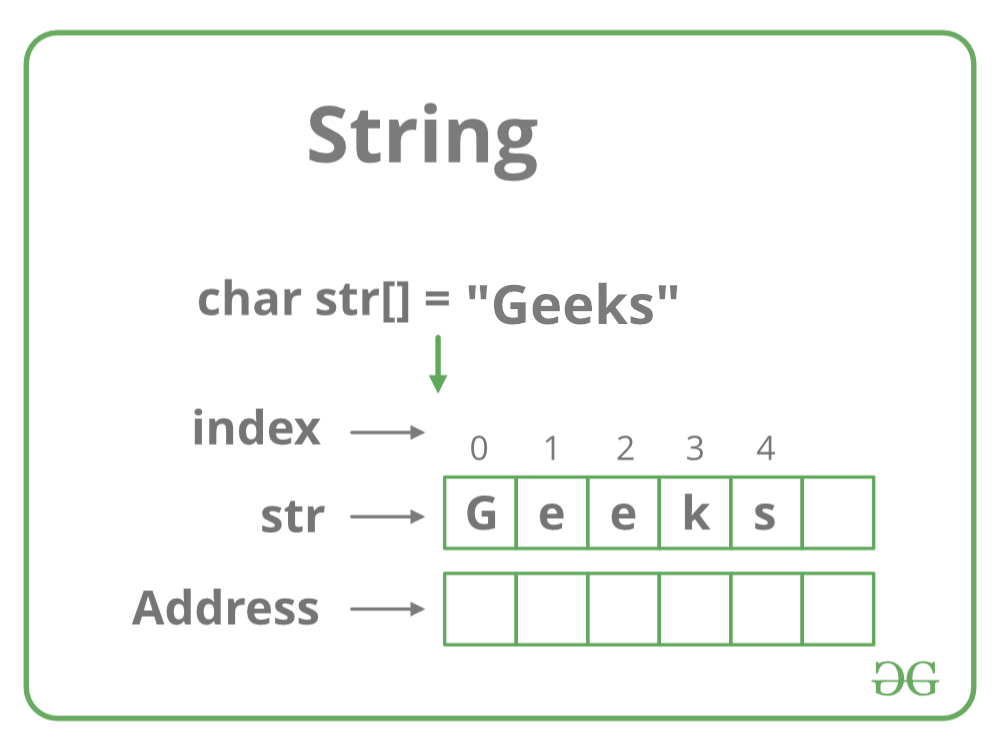
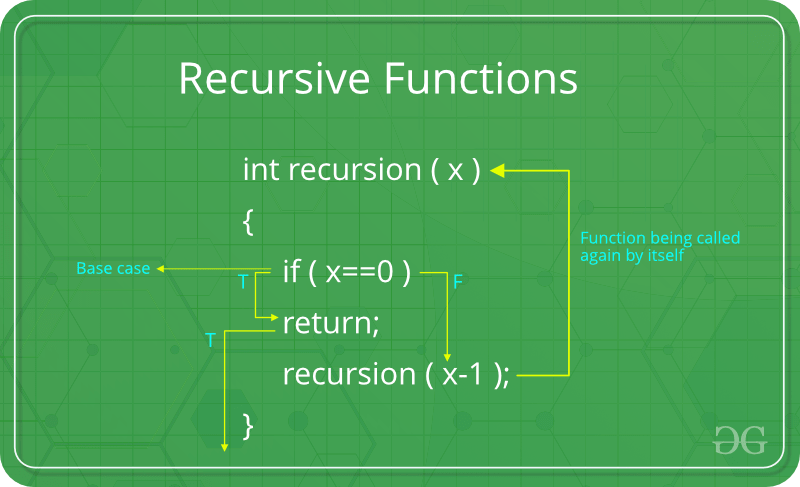
What is a Data Structure?
A data structure is a way of organizing data so that
the data can be used efficiently. Different kinds of data structures are suited to different kinds of
applications, and some are highly specialized for specific tasks. For example, B-trees are particularly
well-suited for the implementation of databases, while compiler implementations usually use hash tables to
look up identifiers. (Source: Wiki Page)
What are linear and non-linear data Structures?
- Linear: A data structure is said to be linear if its elements form a sequence or a linear list. Examples: Array. Linked List, Stacks and Queues
- Non-Linear: A data structure is said to be non-linear if the traversal of nodes is nonlinear in nature. Example: Graph and Trees.
What are the various operations that can be performed on different Data Structures?
- Insertion ? Add a new data item in the given collection of data items.
- Deletion ? Delete an existing data item from the given collection of data items.
- Traversal ? Access each data item exactly once so that it can be processed.
- Searching ? Find out the location of the data item if it exists in the given collection of data items.
- Sorting ? Arranging the data items in some order i.e. in ascending or descending order in case of numerical data and in dictionary order in case of alphanumeric data.
How is an Array different from Linked List?
- The size of the arrays is fixed, and Linked Lists are Dynamic in size.
- Inserting and deleting a new element in an array of elements is expensive, Whereas both insertion and deletion can easily be done in Linked Lists.
- Random access is not allowed on Linked Listed.
- Extra memory space for a pointer is required with each element of the Linked list.
- Arrays have a better cache locality that can make a pretty big difference in performance.
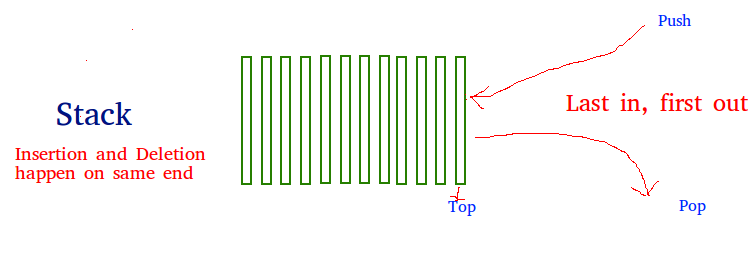
What is Stack and where it can be used?
Stack is a linear data structure in which
the order LIFO(Last In First Out) or FILO(First In Last Out) for accessing elements. Basic operations of the
stack are: Push, Pop, Peek
Applications of Stack:
- Infix to Postfix Conversion using Stack
- Evaluation of Postfix Expression
- Reverse a String using Stack
- Implement two stacks in an array
- Check for balanced parentheses in an expression
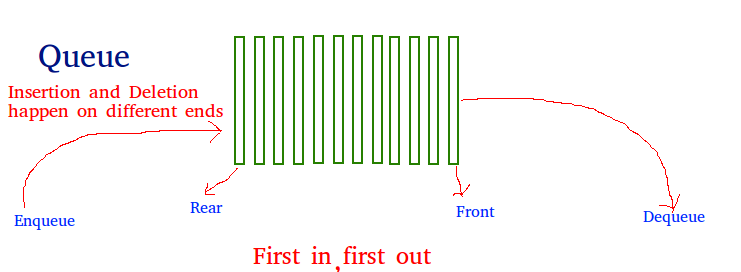
What is a Queue, how it is different from the stack and how is it
implemented?
The queue is a linear structure that
follows the order is First In First Out
(FIFO) to access elements. Mainly the following are basic operations on queue: Enqueue,
Dequeue, Front, Rear
The difference between stacks and queues is in
removing. In a stack we remove the item the most recently added; in a queue, we remove the item the least
recently added. Both Queues and Stacks can be implemented using Arrays and Linked Lists.
What are Infix, prefix, Postfix notations?
- Infix notation: X + Y – Operators are written in between their operands. This is the usual way we write expressions. An expression such as
A * ( B + C ) / D
- Postfix notation (also known as “Reverse Polish notation”): X Y + Operators are written after their operands. The infix expression given above is equivalent to
A B C + * D/
- Prefix notation (also known as “Polish notation”): + X Y Operators are written before their operands. The expressions given above are equivalent to
/ * A + B C D
Converting between these notations: Click here
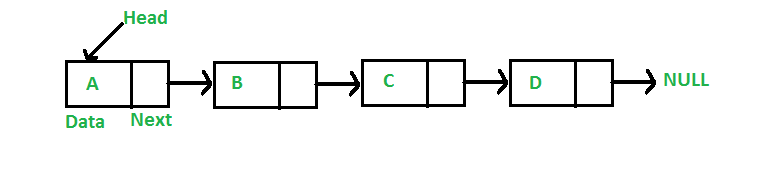
What is a Linked List and What are its types?
A linked list is a linear data structure (like arrays) where each element is a separate object. Each element (that is node) of a list is comprised of two items – the data and a reference to the next node. Types of Linked List :
- Singly Linked List : In this type of linked list, every node stores address or reference of the next node in the list and the last node has next address or reference as NULL. For example 1->2->3->4->NULL
- Doubly Linked List : Here, here are two references associated with each node, One of the reference points to the next node and one to the previous node. Eg. NULL<-1<->2<->3->NULL
- Circular Linked List : Circular linked list is a linked list where all nodes are connected to form a circle. There is no NULL at the end. A circular linked list can be a singly circular linked list or a doubly circular linked list. Eg. 1->2->3->1 [The next pointer of the last node is pointing to the first]
Which data structures are used for BFS and DFS of a graph?
- Queue is used for BFS
- Stack is used for DFS. DFS can also be implemented using recursion (Note that recursion also uses function call stack).
Can doubly-linked be implemented using a single pointer variable in every node?
A
doubly linked list can be implemented using a single pointer. See XOR
Linked List – A Memory Efficient Doubly Linked List
How to implement a stack using queue?
A stack can be implemented using two
queues. Let stack to be implemented be ‘s’ and queues used to implement be ‘q1’ and ‘q2’. Stack ‘s’ can be
implemented in two ways:
- Method 1 (By making push operation costly)
- Method 2 (By making pop operation costly) See Implement Stack using Queues
How to implement a queue using a stack?
A queue can be implemented using two
stacks. Let the queue to be implemented be q and the stacks used to implement q be stack1 and stack2. q can
be implemented in two ways:
- Method 1 (By making enQueue operation costly)
- Method 2 (By making deQueue operation costly) See Implement Queue using Stacks
Which Data Structure Should be used for implementing LRU cache?
We use two data
structures to implement an LRU Cache.
- Queue which is implemented using a doubly-linked list. The maximum size of the queue will be equal to the total number of frames available (cache size). The most recently used pages will be near the rear end and the least recent pages will be near the front end.
- A Hash with page number as key and address of the corresponding queue node as value. See How to implement LRU caching scheme? What data structures should be used?
How to check if a given Binary Tree is BST or not?
If inorder traversal of a
binary tree is sorted, then the binary tree is BST. The idea is to simply do inorder traversal and while
traversing keep track of previous key value. If current key value is greater, then continue, else return
false. See A
program to check if a binary tree is BST or not for more details.
Linked List Questions
- Linked List Insertion
- Linked List Deletion
- middle of a given linked list
- Nth node from the end of a Linked List
Tree Traversal Questions
Convert a DLL to Binary Tree in-place
See In-place
conversion of Sorted DLL to Balanced BST
Convert Binary Tree to DLL in-place
See Convert a
given Binary Tree to Doubly Linked List | Set 1, Convert a
given Binary Tree to Doubly Linked List | Set 2
Delete a given node in a singly linked list
Given
only a pointer to a node to be deleted in a singly linked list, how do you delete it?
Reverse a Linked List
Write a
function to reverse a linked list
Detect Loop in a Linked List
Write a C
function to detect loop in a linked list.
Which data structure is used for dictionary and spell checker?
Data Structure for
Dictionary and Spell Checker?